
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Benefits
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy promotes healing of wounds by enabling new tissue growth, reducing swelling, decreasing inflammation at the wound site and accelerating the healing process within the wound itself.
In cases of compromised blood flow, hyperbaric oxygen therapy forces increased oxygen levels into areas where blood flow is decreased.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy also helps to fight infection in problem wounds while increasing the effects of antibiotics.
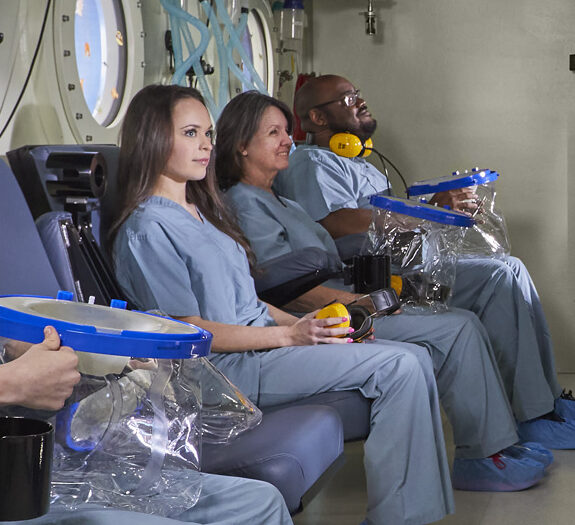

Our Providers may prescribe hyperbaric oxygen therapy as part of the overall treatment plan. Indications for HBOT include, but are not limited to:
- Diabetic Lower Extremity Wounds
- Skin Graft or Flap Preservation
- Soft Tissue Radiation Injury
- Delayed Effect Radiation Injury
- Osteoradionecrosis
- Osteomyelitis (Bone Infections)
- Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Compartment Syndrome
- Crush Injuries
- Non-Healing Surgical Wounds
Detailed Treatment Information
Diabetic Ulcers
Diabetic ulcers, or diabetic wounds, occur in about 15% of the population of people with diabetes (according to the American Podiatric Medical Association). A diabetic ulcer is an open sore that does not heal. Usually, the ulcers present themselves due to a lack of sensation in the patient’s foot or leg due to diabetic neuropathy.
Neuropathy is a condition that affects nerve-ending function in diabetics and impairs sensation. Often, a person with diabetic neuropathy will injure themselves and not notice until the wound is significant because they do not feel it. Also, due to a lack of blood flow and oxygenation to the affected area, these diabetic ulcers often do not heal on their own without professional medical intervention.
The risk of amputation of the affected limb for people with diabetic ulcers is significant if the wound does not show improvement over time. Fortunately, there are ways to treat diabetic ulcers, including surgical debridement (removing the dead tissue around the wound) by a physician or trained medical professional, removing pressure from the wound, and antibiotics, to name a few.
If the wound is still severe and not showing improvement after 30 days, hyperbaric oxygen therapy is an adjunctive (additional) treatment that may be prescribed by the physician and is covered by most insurance plans.
The role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) in the treatment of diabetic ulcers or diabetic wounds has been studied for decades. The results show that hyperbaric oxygen therapy is beneficial in preventing amputation and promoting healing by increasing new capillary growth, reducing swelling (or edema), and increasing blood flow to the affected area. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has also been shown to increase the effectiveness of antibiotics. HBOT is particularly beneficial for patients with a non-healing wound who have undergone debridement and traditional wound care methods which are not showing significant progress after 30 days.
Delayed Radiation Injuries: Radiation Cystitis, Radiation Proctitis, Osteoradionecrosis
Radiation Injury, or soft tissue radiation injury, is a condition in which radiation therapy has been used to fight cancer in the affected area. Still, in doing so, some of the surrounding tissue has been affected by radiation therapy. Approximately 5 percent of the population receiving radiation therapy experience a radiation injury at some point. Radiation injury causes the blood vessels to narrow in the area, depriving oxygen and blood flow to the surrounding tissue. Over time, the lack of essential oxygen and blood flow causes the tissue to break down, resulting in side effects such as pain and wounds.
Radiation Cystitis
Radiation injury of the bladder is called Radiation Cystitis. If the condition is accompanied by bleeding, it is called Hemorrhagic Radiation Cystitis. Other symptoms of Radiation Cystitis are pain and incontinence.
Radiation Proctitis, Radiation Enteritis, Radiation Colitis
Radiation injury of the lower GI tract can be called Radiation Proctitis, Radiation Enteritis, or Radiation Colitis, depending upon where the injury occurred in the GI tract. Common symptoms include pain, incontinence, diarrhea, and bleeding. In some instances, a fistula can occur. Fistulas are wounds directly connected to the bowels.
Osteoradionecrosis
Osteoradionecrosis is a radiation injury of the head and neck area, including a damaged jawbone and tissues of the head and neck. When muscle and skin are compromised, it is called Soft Tissue Radionecrosis.
Radiation injury can occur elsewhere on the body, such as the chest or breasts, after radiation is used to treat breast cancer. Anywhere radiation therapy is used on the body may be susceptible to radiation injury.
In clinical trials, hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been shown to reverse the effects of radiation injury. It has been used for over 30 years to treat radiation injuries.
